nCounter® Autoimmune Discovery Panel
Helping Your Research
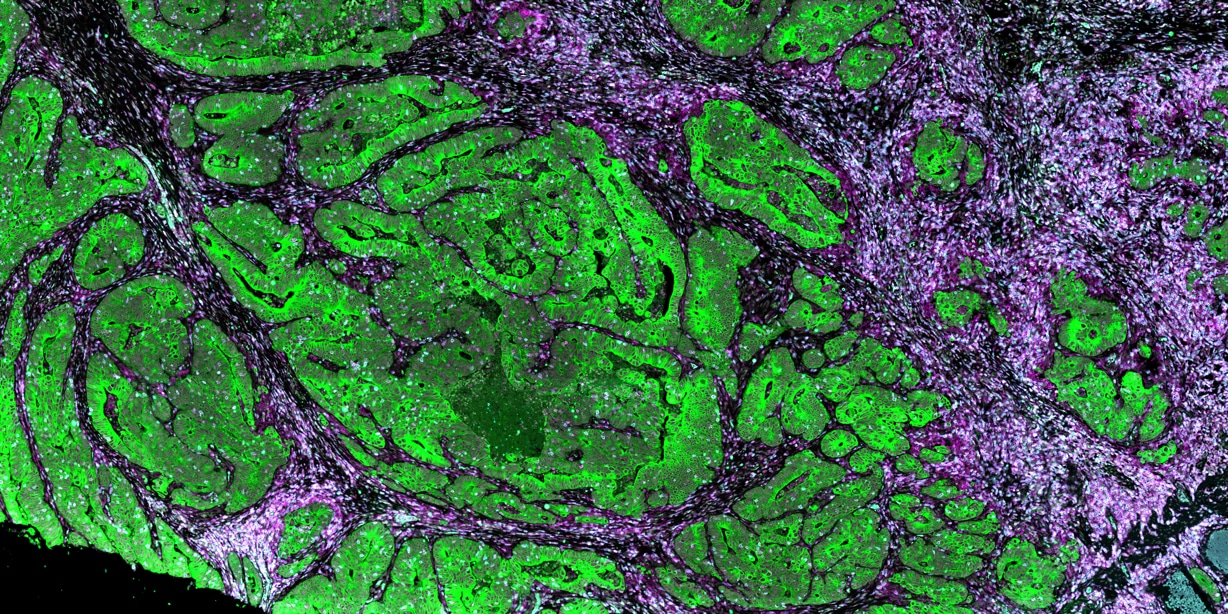
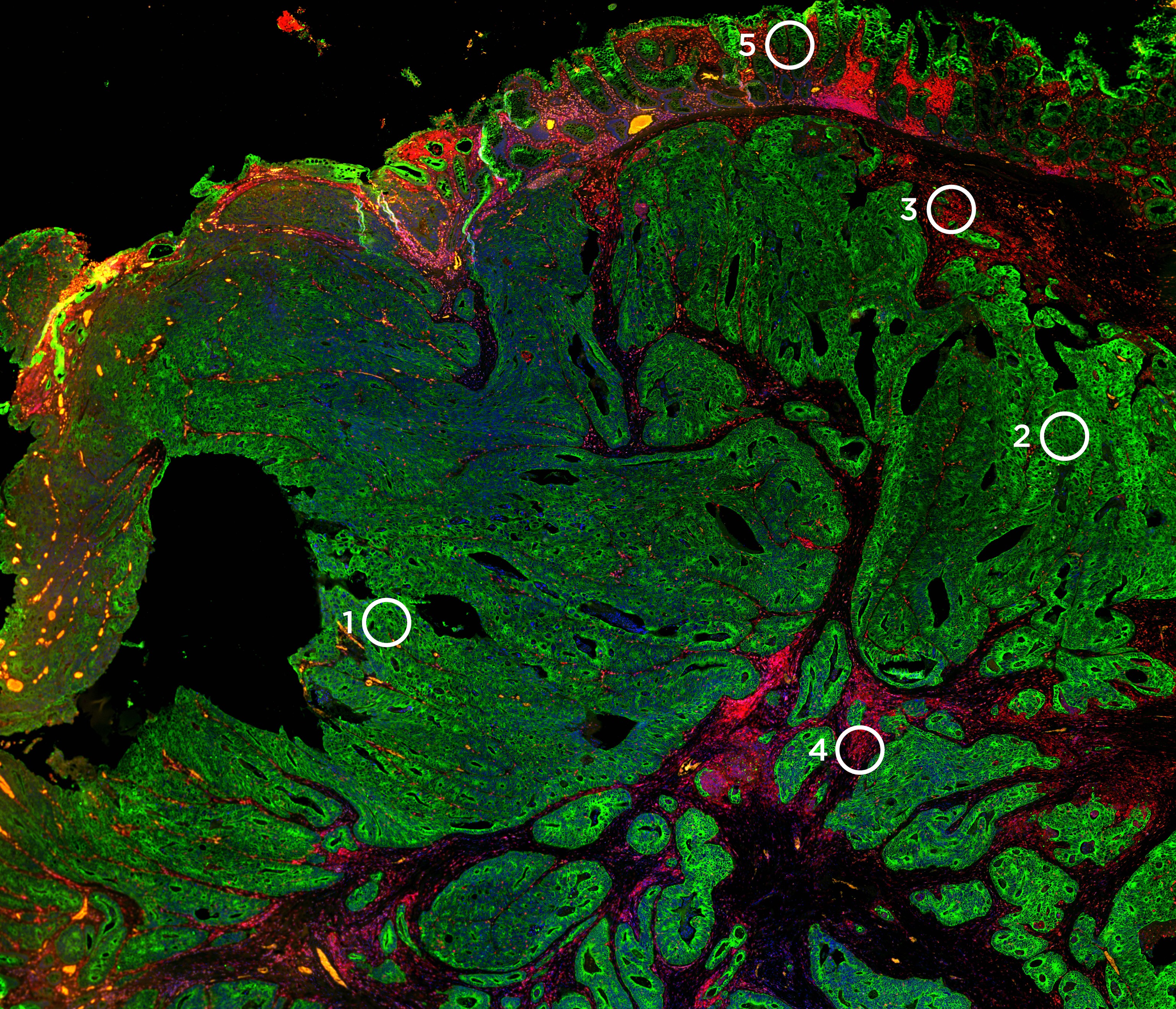
The nCounter Autoimmune Discovery Panel is designed to enable researchers to discover links between known autoimmune disease associated germline variants and gene expression. The genes were selected in collaboration with leading autoimmune researchers and are linked to the top nine autoimmune diseases.
This panel is a Curated Gene List: application and pathway-specific content pre-designed and developed by NanoString available for custom ordering. You can add up to 55 gene targets to it with a “Plus” option to customize the panel to your research project.

Panel Selection Tool
Find the gene expression panel for your research with Panel Pro
Find Your Panel
Product Information
Coverage of Autoimmune Diseases
Disease-specific annotations for nine autoimmune disease types and human immune response genes were assigned across all genes in the autoimmune discovery panel, allowing for the identification of gene functions and signatures for all autoimmune diseases.
Publications
Conjunctival transcriptomics in ocular mucous membrane pemphigoid
PURPOSE: Ocular Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid (OcMMP) is an orphan disease characterized by chronic autoimmune-driven conjunctival inflammation leading to progressive scarring, debilitating symptoms, and blinding sequelae. This feasibility study aims to demonstrate conjunctival genetic transcriptomic analyses as a putative tool for interrogation of pathogenic signaling pathways in OcMMP.
Preclinical Evidence for the Glucocorticoid-Sparing Potential of a Dual Toll-Like Receptor 7/8 Inhibitor in Autoimmune Diseases
Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 and TLR8 are single-stranded RNA-sensing endosomal pattern recognition receptors that evolved to defend against viral infections. However, aberrant TLR7/8 activation by endogenous ligands has been implicated in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases including systemic lupus erythematosus.
Therapeutically expanded human regulatory T-cells are super-suppressive due to HIF1A induced expression of CD73
The adoptive transfer of regulatory T-cells (Tregs) is a promising therapeutic approach in transplantation and autoimmunity. However, because large cell numbers are needed to achieve a therapeutic effect, in vitro expansion is required.
Request a Quote
Contact our helpful experts and we’ll be in touch soon.