CosMx™ Protein Assays
High Resolution Spatial Proteomic Analysis
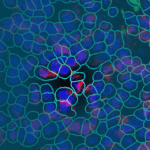
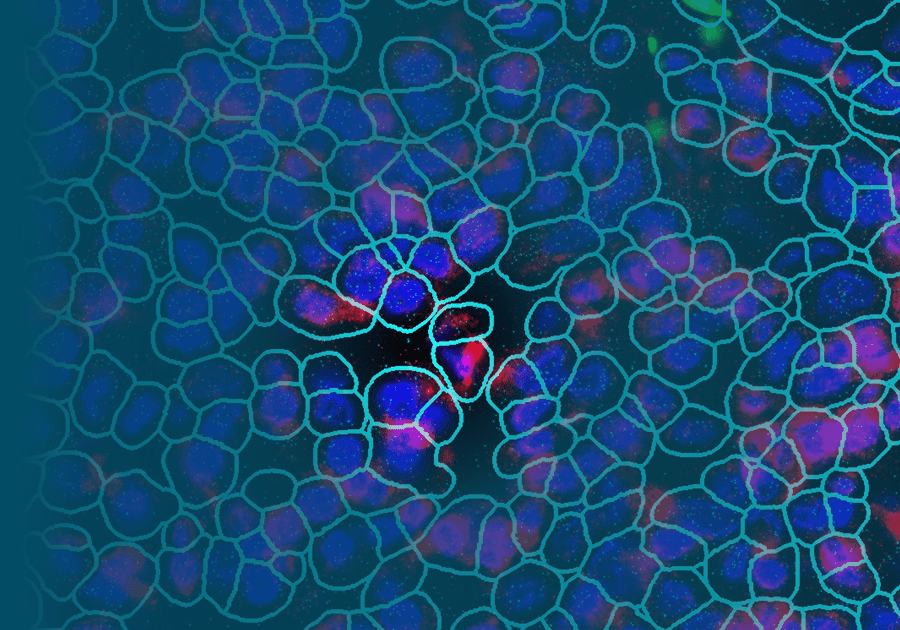
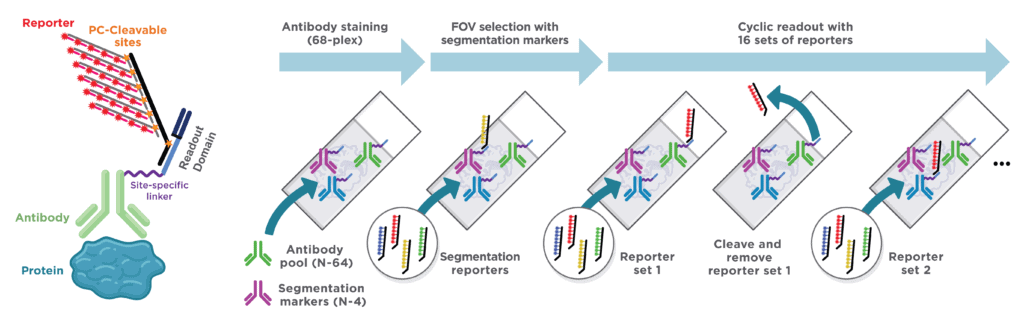
CosMx™ Protein Assays enable high-plex analysis of up to 68 proteins from a single FFPE slide with spatial context at single-cell resolution. CosMx Protein Assays provide unbiased spatial proteomic analysis of tissue sections to expand the number of markers you can profile compared to traditional immunohistochemical and immunofluorescent methods. All CosMx Protein Assays are validated for use in multiplex, so you can focus on the biology of interest without wasting time troubleshooting assay performance.
The CosMx™ SMI and decoder probes are not offered and/or delivered to the Federal Republic of Germany for use in the Federal Republic of Germany for the detection of cellular RNA, messenger RNA, microRNA, ribosomal RNA and any combinations thereof in a method used in fluorescence in situ hybridization for detecting a plurality of analytes in a sample without the consent of the President and Fellows of Harvard College (Harvard Corporation) as owner of the German part of EP 2 794 928 B1. The use for the detection of cellular RNA, messenger RNA, microRNA, ribosomal RNA and any combinations thereof is prohibited without the consent of the President and Fellows of Harvard College (Harvard Corporation).
Publications
Exploring Markers of Exhausted CD8 T Cells to Predict Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Background: Reversal of CD8 T-cell exhaustion was considered a major antitumor mechanism of anti-programmed cell death-1 (PD-1)/ anti-programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1)-based immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. Objectives: The aim of this study was to identify markers of T-cell exhaustion that is best associated with ICI treatment efficacy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Discovery of CD80 and CD86 as recent activation markers on regulatory T cells by protein-RNA single-cell analysis
Background: Traditionally, the transcriptomic and proteomic characterisation of CD4+ T cells at the single-cell level has been performed by two largely exclusive types of technologies: single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) and antibody-based cytometry. Here, we present a multi-omics approach allowing the simultaneous targeted quantification of mRNA and protein expression in single cells and investigate its performance to dissect the heterogeneity of human immune cell populations.
MiR130b from Schlafen4+ MDSCs stimulates epithelial proliferation and correlates with preneoplastic changes prior to gastric cancer
The myeloid differentiation factor Schlafen4 (Slfn4) marks a subset of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the stomach during Helicobacter-induced spasmolytic polypeptide-expressing metaplasia (SPEM). Objective: To identify the gene products expressed by Slfn4+-MDSCs and to determine how they promote SPEM.
Related Resources