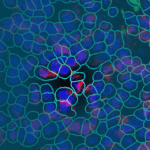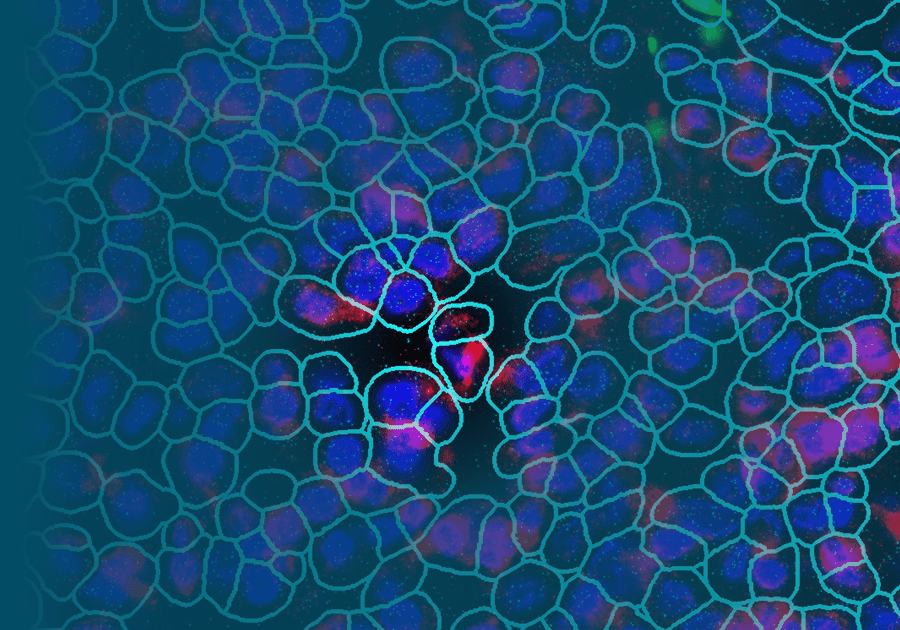
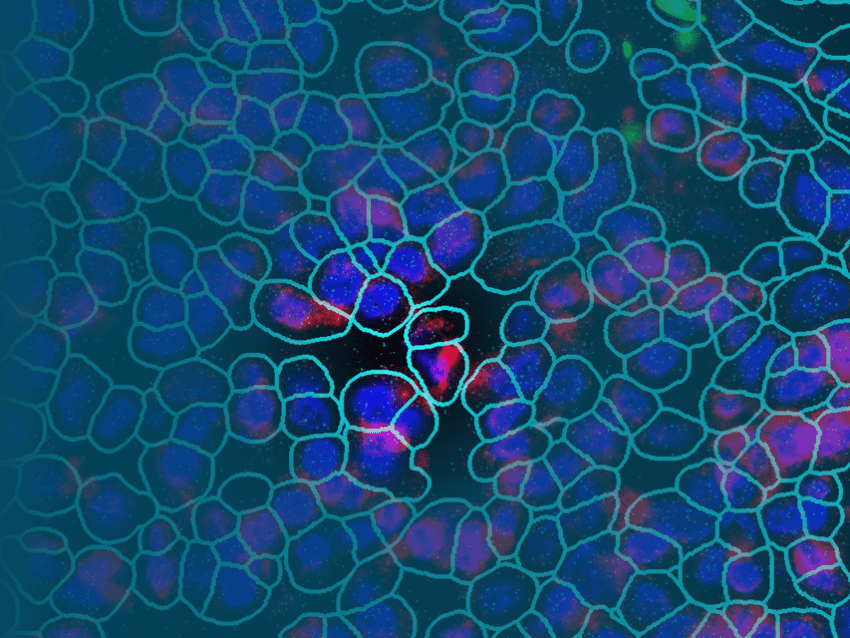
CosMx™ Mouse Neuroscience Panel
The CosMx™ SMI and decoder probes are not offered and/or delivered to the Federal Republic of Germany for use in the Federal Republic of Germany for the detection of cellular RNA, messenger RNA, microRNA, ribosomal RNA and any combinations thereof in a method used in fluorescence in situ hybridization for detecting a plurality of analytes in a sample without the consent of the President and Fellows of Harvard College (Harvard Corporation) as owner of the German part of EP 2 794 928 B1. The use for the detection of cellular RNA, messenger RNA, microRNA, ribosomal RNA and any combinations thereof is prohibited without the consent of the President and Fellows of Harvard College (Harvard Corporation).
Helping Your Research
Mouse Single-Cell Spatial RNA Analysis
The CosMx Mouse Neuroscience Panel is designed to provide robust cell typing, cell-cell interaction analysis, and more in mouse brain and other neuronal tissues. Profile expression of 1000 highly curated targets at subcellular resolution and customize with up to 50 of your own targets.
Publications & Posters
Characterizing Late-Onset AD Models Using Spatial Whole Transcriptome Analysis – AGBT 2021
Smarca4-deficient lung cancers display a metastatic-like cell state and a distinct cell-of-origin – AGBT 2021
Opposing immune and genetic mechanisms shape oncogenic programs in synovial sarcoma
Synovial sarcoma (SyS) is an aggressive neoplasm driven by the SS18-SSX fusion, and is characterized by low T cell infiltration. Here, we studied the cancer-immune interplay in SyS using an integrative approach that combines single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), spatial profiling and genetic and pharmacological perturbations.
The spatial landscape of lung pathology during COVID-19 progression
Recent studies have provided insights into the pathology and immune response to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)1–8. However, thorough interrogation of the interplay between infected cells and the immune system at sites of infection is lacking.
Temporal and spatial heterogeneity of host response to SARS-CoV-2 pulmonary infection
The relationship of SARS-CoV-2 pulmonary infection and severity of disease is not fully understood. Here we show analysis of autopsy specimens from 24 patients who succumbed to SARS-CoV-2 infection using a combination of different RNA and protein analytical platforms to characterize inter-patient and intra-patient heterogeneity of pulmonary virus infection.
Related Resources




Support Documents

Contact Us
Have questions or simply want to learn more?
Contact our helpful experts and we’ll be in touch soon.