nCounter® CAR-T Characterization Panel
Helping Your Research
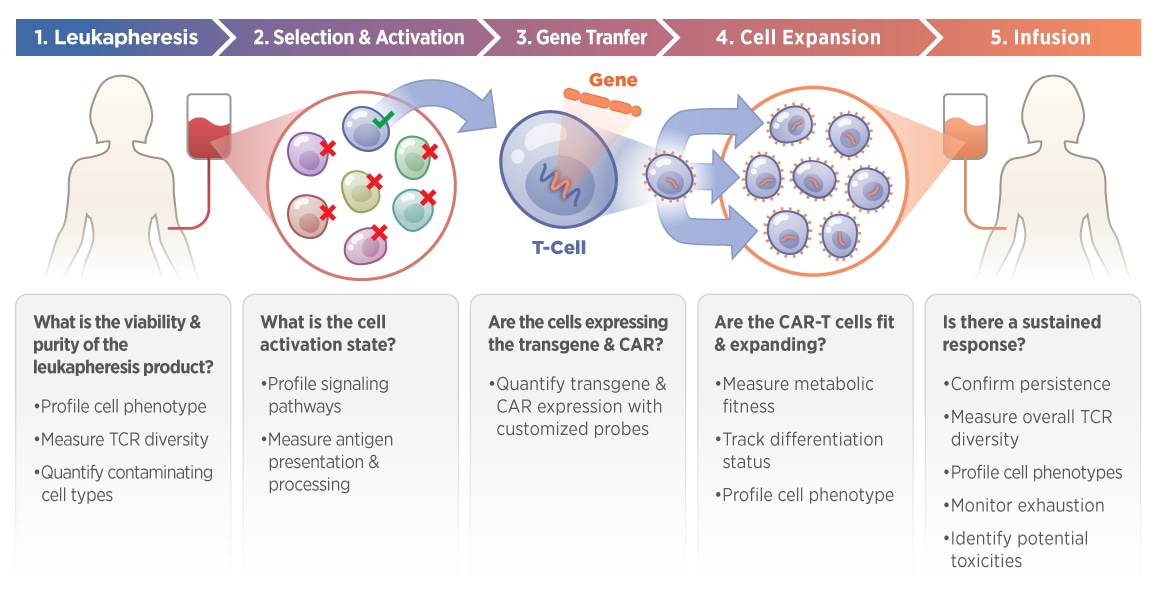
The nCounter CAR-T Characterization Panel was created in collaboration with experts in CAR-T therapy to facilitate the development of robust product release assays. Confidently profile CAR-T products for research and manufacturing applications with an automated, and reproducible assay. Ideally suited for new CAR-T development and QC, the CAR-T Characterization Gene Expression Panel can help streamline the CAR-T manufacturing workflow and potentially reduce vein to vein time. This panel can measure eight essential components of CAR-T biology with 780 human genes.
Empower your knowledge of CAR-T with the most up-to-date biology developed with experts in the field.
- Optimize CAR-T method development
- Create manufacturing acceptance criteria
- Measure metabolic fitness and persistence
- Monitor post-infusion exhaustion and toxicity

Panel Selection Tool
Find the gene expression panel for your research with Panel Pro
Find Your PanelProduct Information
Partnerships
NanoString is excited to be working with Servier (as project leader), Bayer, Janssen, and Takeda as partners with the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) Consortium in the European Union to develop gold standard analytical methods to use throughout development, manufacturing, and delivery of CAR-T cell therapies. The IMI is the largest public-private partnership in the world dedicated to health research.
The TCR Diversity report is available for purchase separately from NanoString for use within the ROSALIND® Platform and evaluates the expression of variable regions of the T cell receptor. The variable regions are assessed for overall expression (above or below background) and normalized to a panel standard which allows for more precise quantification of these variable regions. An estimate of TCR Diversity is calculated and shown relative to designated grouping variables.
The TCR score calculates the diversity of T cell receptor beta variable regions within a sample. The score is based on the Shannon Diversity index calculation, a mathematical measure of species diversity within a community. This ecological calculation accounts for the abundance and evenness of the variable regions present within a given sample versus the population of T cell receptors within a given dataset. A given score is relative within a dataset, and a higher TCR score means there is a more diverse population of variable regions or a less clonal population. A lower TCR score means there is less diversity or a more clonal population. True clonality can only be determined by full sequencing of the T cell receptors, but clonality can be estimated by measuring the diversity of TCR beta variable regions.
Download a demo version of the TCR Diversity Report and open the corresponding TCR Diversity Report-Readme file.


ROSALIND is a cloud-based platform that enables scientists to analyze and interpret differential gene expression data without the need for bioinformatics or programming skills. ROSALIND makes analysis of nCounter data easy, with guided modules for:
- Normalization
- Quality Control
- Individual Pathway Analysis
- Differential Expression
- Gene Set Analysis
nCounter customers can access ROSALIND free of charge.

Related Resources




Publications
Two Cases of Severe Pulmonary Toxicity from Highly Active Mesothelin-Directed CAR T Cells
Multiple clinical studies have treated mesothelin (MSLN)-positive solid tumors by administering MSLN-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. Although these products are generally safe, efficacy is limited.
Biological and Clinical Implications of Gene-Expression Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Proposal for a Targeted BLYM-777 Consortium Panel as Part of a Multilayered Analytical Approach
Simple Summary: This review summarizes gene-expression profiling insights into the background and origination of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL). To further unravel the molecular biology of these lymphomas, a consortium panel called BLYM-777 was designed including genes important for subtype classifications, genetic pathways, tumor-microenvironment, immune response and resistance to targeted therapies.
Molecular and Functional Signatures Associated with CAR T Cell Exhaustion and Impaired Clinical Response in Patients with B Cell Malignancies
Despite the high rates of complete remission following chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, its full capacity is currently limited by the generation of dysfunctional CAR T cells. Senescent or exhausted CAR T cells possess poor targeting and effector functions, as well as impaired cell proliferation and persistence in vivo.
Request a Quote
Contact our helpful experts and we’ll be in touch soon.