Unravel the Complexity of Neuroscience
Neuroscience is a complex field that involves studying highly specialized cells and tissue structures that work together in concert. Researchers study the morphology, structure, and spatial organization of neurons to better understand neuronal development. They look for relevant biomarkers for the onset and progression of neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation as well as novel targets for therapeutics. Cell atlases of the brain are mapped to explain how different cell types such as neurons, microglia, and oligodendrocytes interact with each other as well as peripheral immune cells.
Challenges
We are just beginning to unravel the secrets behind the function of the Central Nervous System (CNS). Many different cell types interact with each other in a choreographed manner. Preclinical models and developmental biology give us some insight into the biology of the CNS, but it can be challenging to find suitable animal models. The immune response to infectious disease, neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration in the CNS doesn’t fit the same paradigm as the systemic immune response due to the blood brain barrier. Add to this the fact that brain samples are scarce and neuroscience research becomes particularly difficult to navigate.
Disease Characterization
Preclinical Models
Drug Discovery
Your Trusted Partner for Neuroscience Research
NanoString’s integrated, multiomic research solutions allow you to study neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and neuronal development from the level of single cells to multicellular tissue compartments and patient cohorts. Wherever you are headed with your neuroscience research, we can get you actionable insights from FFPE, fresh frozen tissue, cell lysates, and biofluids. Profile the expression of 800+ genes from a single sample with the nCounter® Analysis System. Spatially profile the whole transcriptome and select protein targets within distinct tissue compartments and cell populations with the GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler (DSP). Obtain the highest plex single cell and subcellular spatial multiomics data with the CosMx® Spatial Molecular Imager (SMI).
NanoString has been developing innovative research tools for over 20 years and we believe in partnering with you to enable your research.
The CosMx® SMI and decoder probes are not offered and/or delivered to the Federal Republic of Germany for use in the Federal Republic of Germany for the detection of cellular RNA, messenger RNA, microRNA, ribosomal RNA and any combinations thereof in a method used in fluorescence in situ hybridization for detecting a plurality of analytes in a sample without the consent of the President and Fellows of Harvard College (Harvard Corporation) as owner of the German part of EP 2 794 928 B1. The use for the detection of cellular RNA, messenger RNA, microRNA, ribosomal RNA and any combinations thereof is prohibited without the consent of the President and Fellows of Harvard College (Harvard Corporation).
One Suite of Tools. Unlimited Potential.

nCounter®
Analysis System
- Discover predictive and prognostic biomarkers
- Develop signatures associated with neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders
- Evaluate mechanisms of treatment response
- Monitor disease biomarkers in clinical trials
- Screen cells for drug development

GeoMx®
Digital Spatial Profiler
- Discover and develop spatial gene signatures
- Characterize the heterogeneity of brain tissue in health and disease
- Study the effect of plaques and neurofibrillary tangles on astrocytes and microglia
- Characterize the localized treatment response
- Study the localized response to infectious disease in the brain
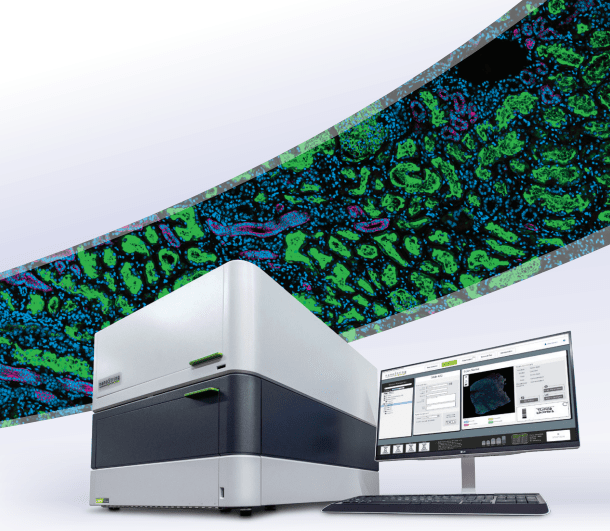
CosMx®
Spatial Molecular Imager
- Discover unique functions of different cell types in the brain and peripheral nervous system
- Discover unique cell-cell interactions
- Define cellular neighborhoods
- Reveal functional, cellular, and temporal changes spatially at single-cell and subcellular resolution
- Characterize axonal growth, neuronal migration, and synapse formation
A Holistic View of Neuroscience Across Multiple Dimensions
NanoString’s collection of assays across all three of our platforms delivers a family of multiplex gene and protein expression assays for bulk and spatial analysis in human and mouse samples that support basic and translational studies on CNS development, health, and disease. Curated content for Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Stroke, Traumatic Brain Injury, and Multiple Sclerosis (MS) enables you to gain a holistic understanding of the function and molecular biology of neuronal cell types across the brain and peripheral nervous system.
Select nCounter Neuroscience Gene Expression Panels
The nCounter Neuroscience portfolio includes several curated, off-the-shelf panels that cover the pathways and markers involved in neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, and the biology of glial cells. Create a panel from scratch for targets from any species by working with our bioinformatics team to develop probes for a Custom CodeSet or spike in up to 55 targets of your choice to any off-the-shelf panel.
GeoMx DSP Assays for Neuroscience
Spatially profile expression of the human or mouse transcriptome in select tissue structures or cell populations in FFPE or fresh frozen tissue sections or profile select protein targets involved in neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders. Take advantage of the Spatial Proteogenomics workflow to discover novel multiomic biomarkers by spatially profiling RNA and protein simultaneously from the same tissue section.
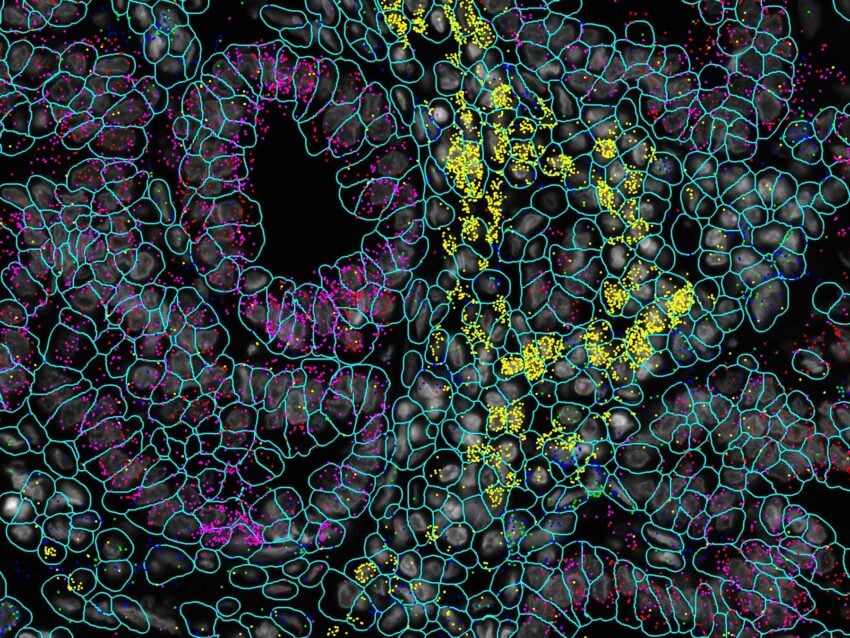
CosMx SMI Assays for Neuroscience Research
CosMx assays for neuroscience research include a 1000 plex RNA panel for human or mouse that includes markers for robust cell and tissue typing, ligand-receptor interactions, metabolism, circadian rhythm, antigen presentation, cell damage, stress response, and wound healing. For studying mouse models of neurological disease you can profile 1000 highly curated RNA targets with the Mouse Neuroscience Panel or 68 proteins with the Mouse Neuroscience Protein Panel.
Spotlight on Success
“The GeoMx DSP is a workhorse in the lab for hypothesis testing… Complementing the single-neuron resolution of GeoMx, we rely on the CosMx SMI to achieve true subcellular spatial analyses and uncover cell-cell interactions… NanoString’s consistent advancements in panel development and plexity provide us with the confidence that they will continue empowering neuroscientists to explore complex questions.”

Miranda Orr, PhD
Assistant Professor, Gerontology and Geriatric Medicine, Wake Forest School of Medicine
Case Studies
Contact Us
Request more information and we’ll be in touch soon.
Publications
Spatial transcriptomics reveals molecular dysfunction associated with cortical Lewy pathology
A key hallmark of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is Lewy pathology. Composed of α-synuclein, Lewy pathology is found both in dopaminergic neurons that modulate motor function, and cortical regions that control cognitive function.
Digital spatial profiling of segmental outflow regions in trabecular meshwork reveals a role for ADAM15
In this study we used a spatial transcriptomics approach to identify genes specifically associated with either high or low outflow regions in the trabecular meshwork (TM) that could potentially affect aqueous humor outflow in vivo. High and low outflow regions were identified and isolated from organ cultured human anterior segments perfused with fluorescently-labeled 200 nm FluoSpheres.
Clinically relevant molecular hallmarks of PFA ependymomas display intratumoral heterogeneity and correlate with tumor morphology
Posterior fossa type A (PF-EPN-A, PFA) ependymoma are aggressive tumors that mainly affect children and have a poor prognosis. Histopathology shows significant intratumoral heterogeneity, ranging from loose tissue to often sharply demarcated, extremely cell-dense tumor areas.